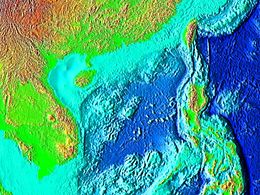

The Philippines, China, Brunei, Vietnam, Taiwan and Malaysia have overlapping claims in the South China Sea. The biggest contested area is the Spratly group of islands, which are believed to be rich in oil, mineral and marine resources. The South China Sea is thought to hold huge reserves of gas and oil, estimated by some United States surveys at nearly twice as much as China’s current known reserves of oil.
The Philippines is pushing ASEAN members to take a stand against China’s claim to the entire South China Sea. ASEAN members include Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam.
Under the Philippine plan, countries with claims will map and delineate areas that are in dispute, and those that are not, so that exploration can go ahead in the undisputed areas. The plan for disputed areas is to turn them into areas of joint cooperation for projects between nations.
Meanwhile, Japan has called for a stronger code of conduct. While Japan isn’t a claimant or an ASEAN country, as an economic power in the region it has a stake to keep the South China Sea open as a trade route.