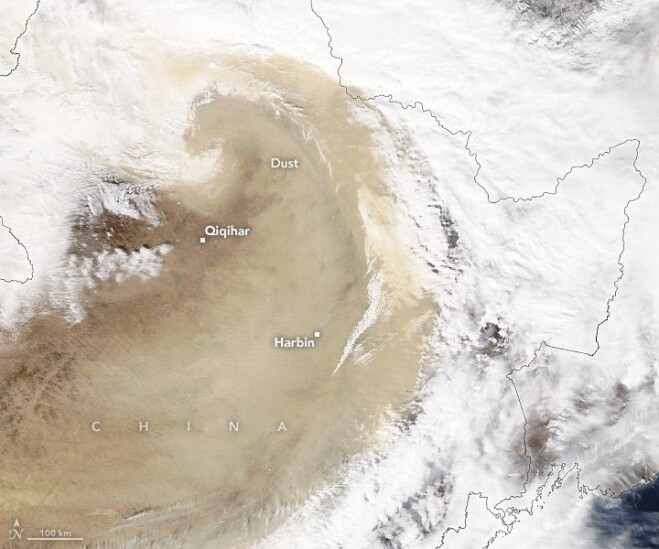
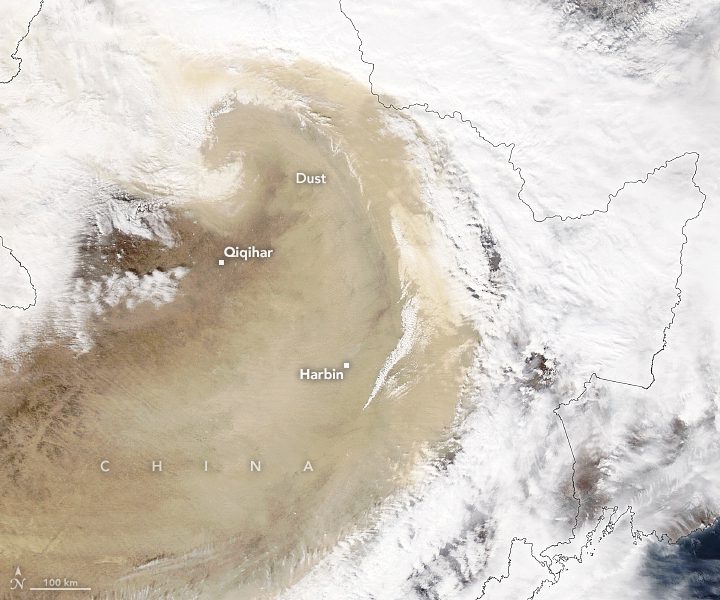
A comma-shaped low-pressure system that pushed across Mongolia and China unleashed a major dust storm in late-March 2023. A tight pressure gradient fueled the strong winds that lifted sand and dust from the Gobi Desert as the system moved into eastern China on March 22. With visibility plummeting in Beijing, air quality sensors measured soaring levels of particulate matter (PM).
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this image showing a thick swirl of dust over China’s Harbin, Changchun, and Shenyang provinces on March 22, 2023. Cyclonic atmospheric circulation appears to have sucked dust into and above the clouds.
The dust has affected more than 560 million people in the densely populated region, according to China’s National Forestry Grassland Administration. In Beijing, which has a population of more than 20 million, the air quality index rose well above 500 for coarse (PM10) particles and above 200 for fine (PM2.5) particles on that day. Those levels are considered “hazardous” and “very unhealthy” to human health.
Image Credit: NASA Earth Observatory image by Lauren Dauphin, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE and GIBS/Worldview.