Using archives of satellite imaging data, a study in Frontiers in Earth Science has conducted the most in-depth study of China’s intertidal wetlands to date and found a 37.62% decrease in area between 1970 and 2015.
Intertidal wetlands significantly contribute to China’s environmental and ecological diversity, but are facing unprecedented pressures from anthropogenic development, as well as the threat of future sea level rise.
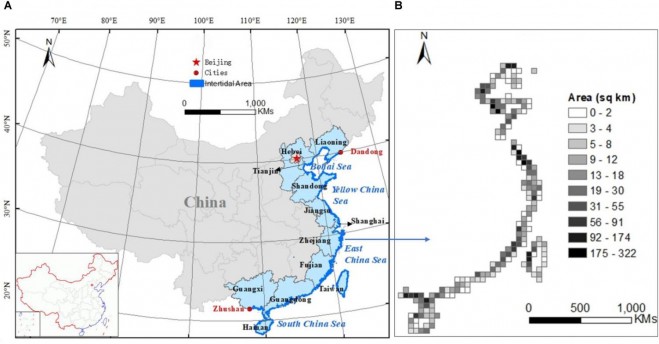
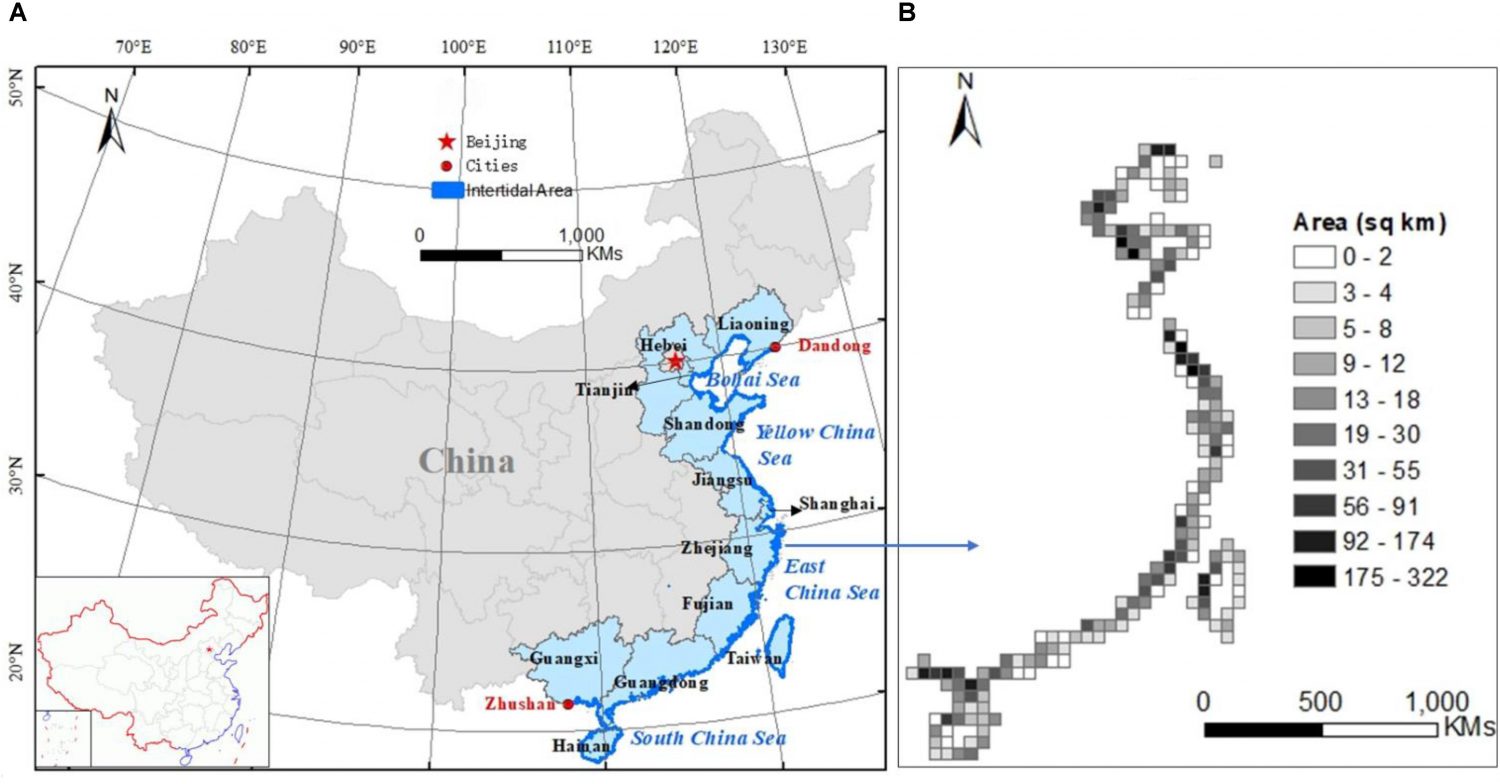
The location of the Chinese intertidal zone (A) and its area distribution at 50-kilometer resolution (B). The location and distribution map are based on 2015 data.
Despite the ecological and economic significance of China’s vast areas of intertidal wetlands, such as storm protection, pollution purification and carbon sequestration, their distribution and variation over time have not been well documented. This study highlights the urgency for conservation measures of these valuable habitats by showing the scale of their decline for the first time.