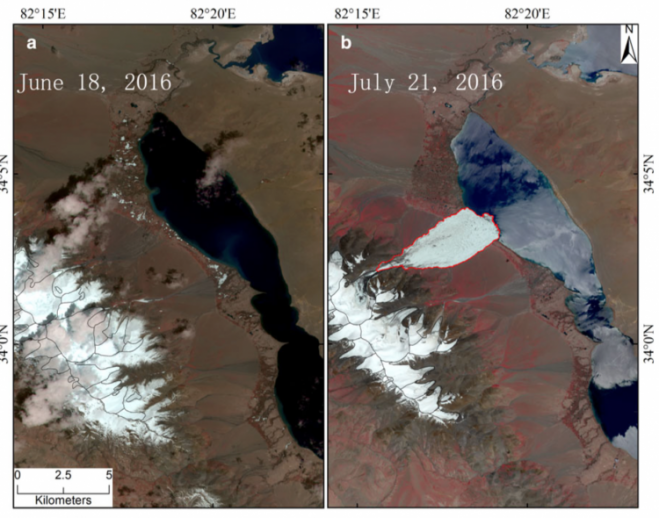
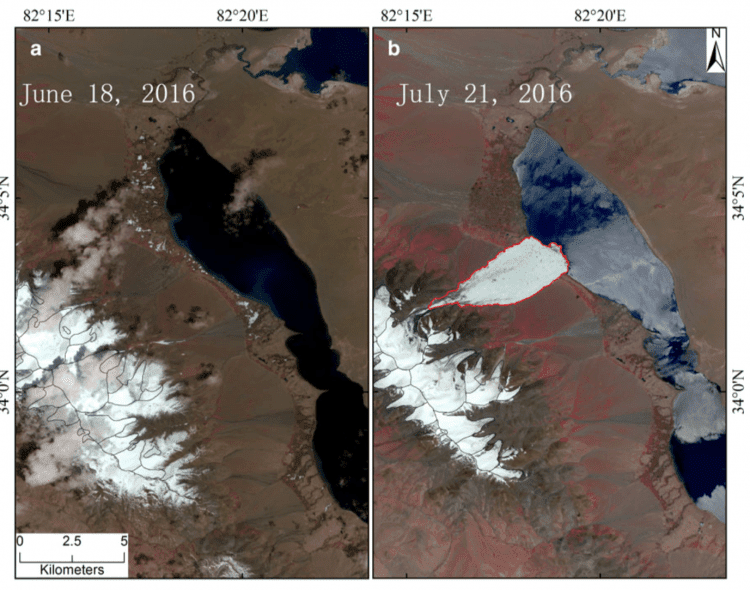
The Journal of Glaciology recently published the first account from scientists at the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (ITPCAS) concerning a glacier that collapsed on July 17, 2016, killing nine local yak herders. Eyewitnesses reported the episode lasted only four to five minutes, but more than 70 million cubic meters of ice tumbled down a mountain valley, spreading across 6 kilometers of the lowland below.
ESA’s Sentinel-2 satellite recorded “before and after” 10-meter-resolution images of the Aru Glacier collapse on July 17, 2016. (Credit: ESA/Sentinel-2)
On Sept. 21, 2016, a neighboring glacier to the southeast collapsed. Although there were no deaths, the volume of ice released was even larger than in the first collapse.ESA’s Sentinel-2 satellite recorded “before and after” 10-meter-resolution images of the Aru Glacier collapse on July 17, 2016. (Credit: ESA/Sentinel-2)
“Unusually heavy snowfalls in the months before the collapses must have played a role,” noted Lide Tian of ITPCAS, lead author of the scientific paper. “Large amounts of resulting meltwater may have found their way to the glacier bed or to some surface of structural weakness within the ice. There the meltwater would have reduced frictional drag and triggered the collapses.”