After an extremely wet October, southeast Australia continued to see heavy rainfall in November 2022. With soils already saturated and dams full, the latest storms have added to ongoing flooding across New South Wales and Victoria.
In the week leading up to Nov. 14, 2022, large parts of New South Wales and Victoria saw more than 50 millimeters of rain (2 inches). The town of Forbes, New South Wales, had the highest daily total for the week. It saw 118 millimeters (4.6 inches) fall in a 24-hour period spanning November 13-14. The abundant rain across the region caused rivers to rise and flood nearby towns. Forbes saw its third major flood event in just four weeks as waters on the Lachlan River rose faster than expected.
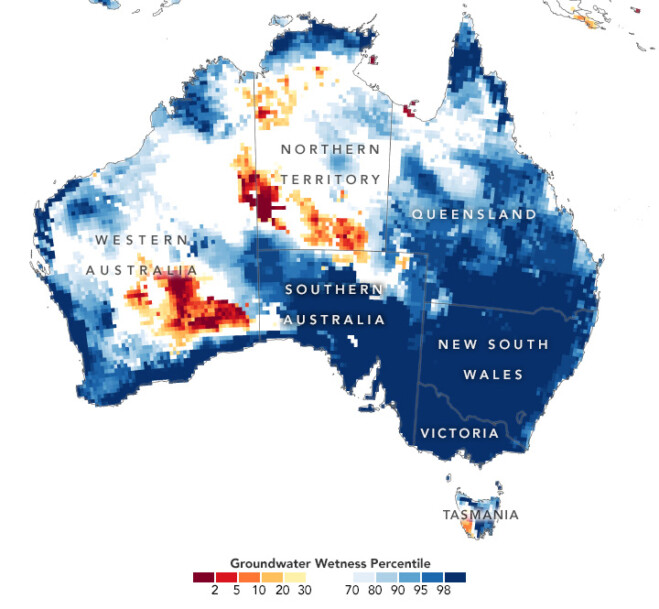
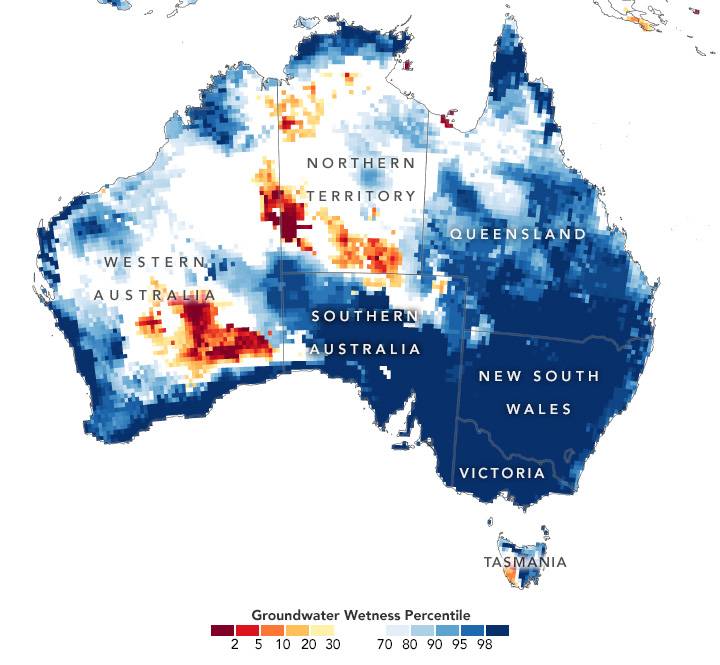
Water that seeps deep into the soil can influence groundwater levels for months. The accompanying map depicts shallow groundwater storage in Australia from Nov. 11-14, 2022, as measured by the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) satellites. The colors depict the wetness percentile; that is, how the levels of groundwater compare to long-term records (1948-2012). Blue areas have more abundant water than usual, and orange and red areas have less.