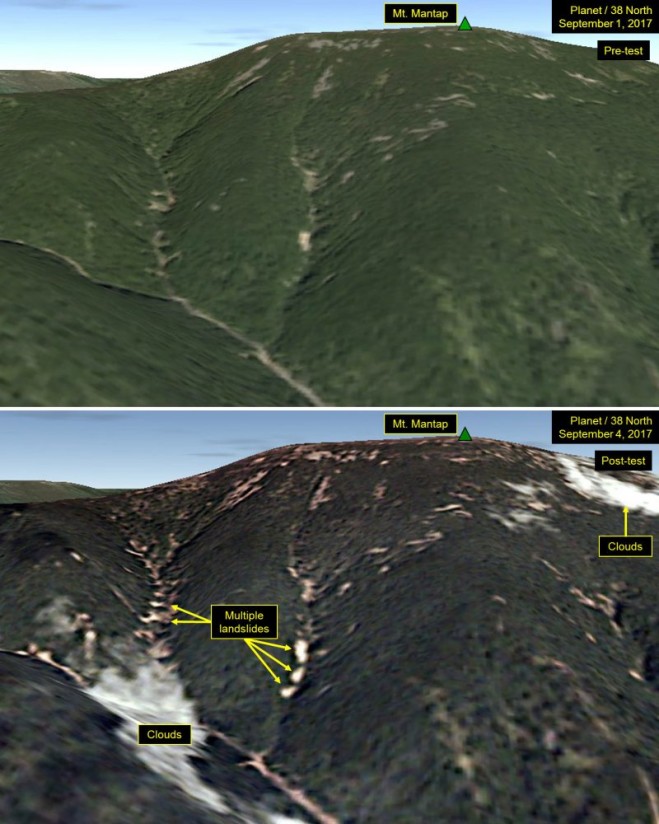
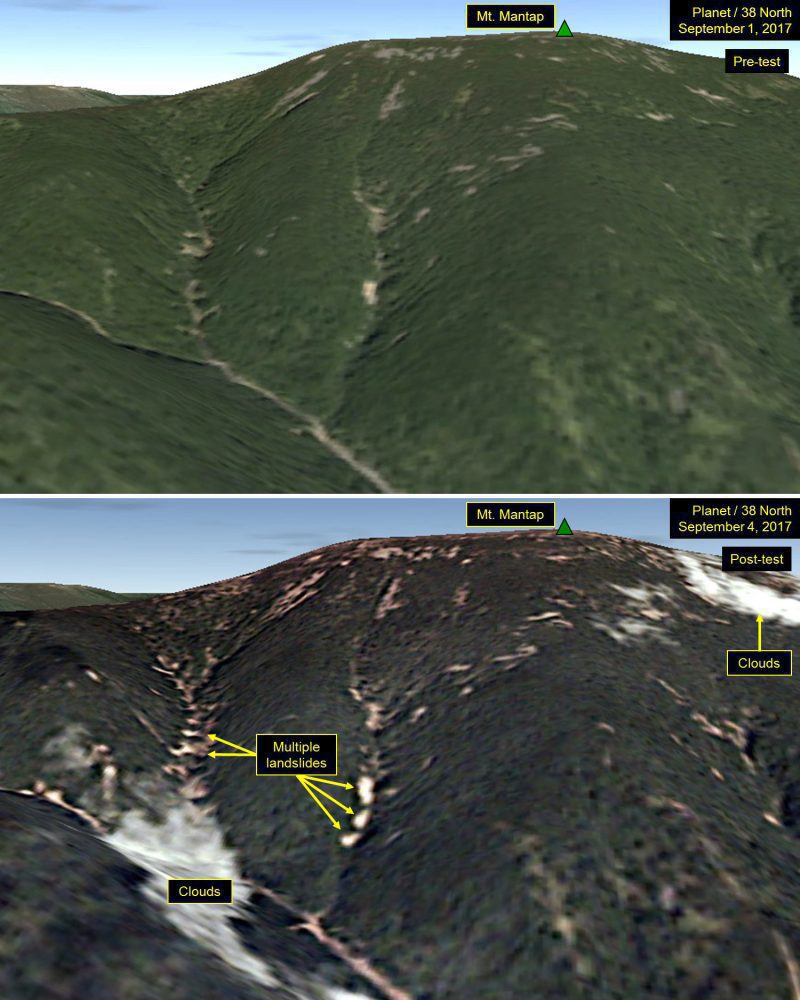
Analysts peering at satellite images of North Korea after its latest nuclear test spotted many landslides and wide disturbances at the country’s test site. Tunnels for the nuclear blasts are deep inside Mount Mantap, a mile-high peak.
“These disturbances are more numerous and widespread than what we have seen from any of the five tests North Korea previously conducted,” three experts wrote in an analysis for 38 North, a website run by the U.S.-Korea Institute of the Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International Studies.
Early readings from global networks that monitor shock waves suggest that the nuclear blast had a destructive power equal to 120,000 tons of high explosives. If correct, that’s roughly six times more powerful than North Korea’s test of September 2016, and eight times larger than the bomb dropped on Hiroshima in 1945.
The new satellite images of the Punggye-ri nuclear test site were taken the day after the nuclear detonation. Planet, a company in San Francisco that owns swarms of tiny satellites, reconnoitered the secretive nuclear test site.
Satellite images show Mount Mantap on Sept. 1, 2017, and Sept. 4, 2017, before and after North Korea’s latest nuclear test deep under the mountain. (Credit: Planet)
Click here for more information.
