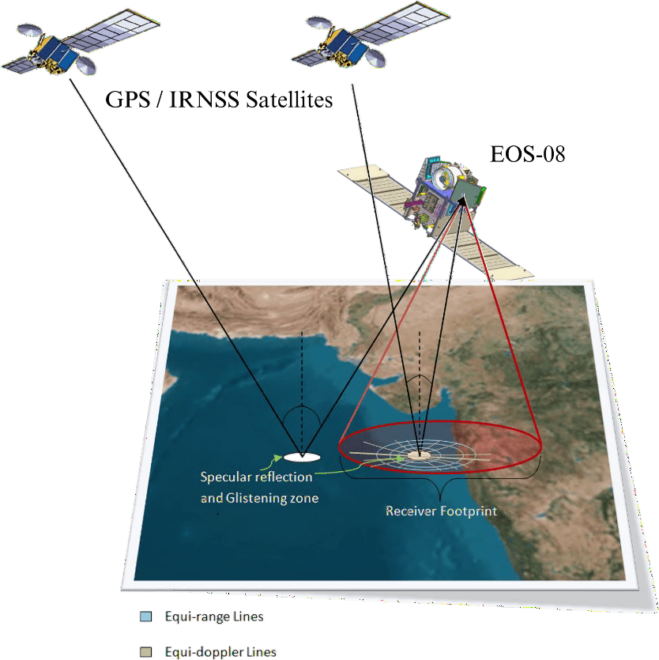
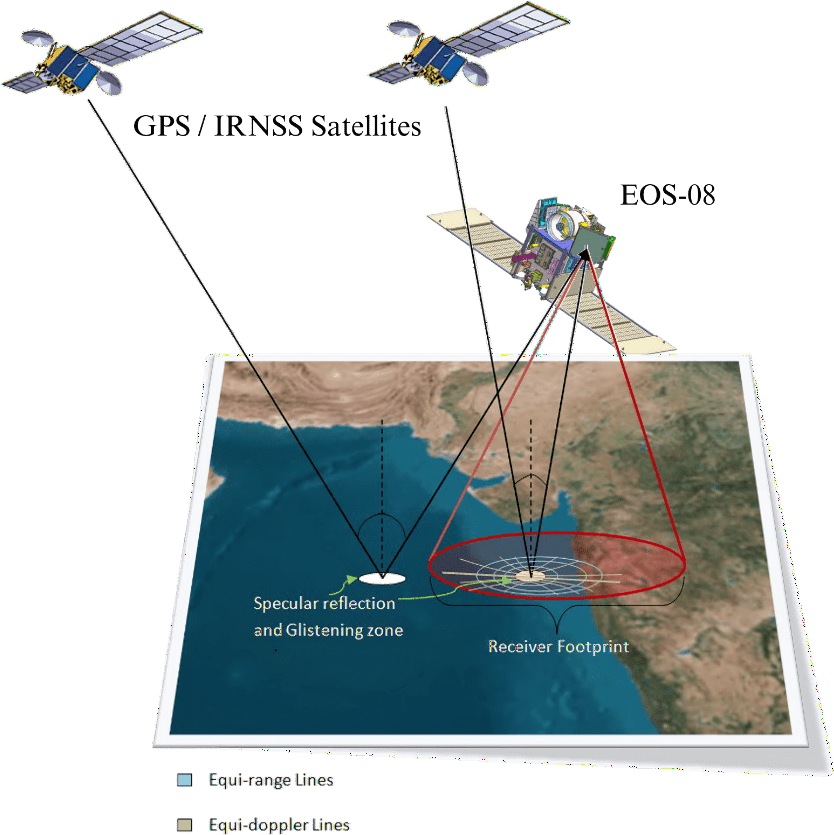
The GNSS-Reflectometry (GNSS-R) instrument on the EOS-08 satellite commenced operations on Aug. 18, 2024. The raw data is being processed at the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC-ISRO) in Shadnagar, Hyderabad, using algorithms and data processing software developed by the Space Applications Centre (SAC-ISRO), Ahmedabad. Multiple levels of data products have been successfully generated.
GNSS-Reflectometry represents a new mode of remote sensing. Signals from Global and Regional Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS/RNSS), such as GPS and NavIC, are reflected off various Earth surfaces, including oceans, agricultural lands and river bodies. These reflected signals are collected by a precision receiver onboard the satellite (see accompanying figure) as it orbits the Earth at an altitude of 475 kilometers. This measurement system operates without dedicated transmitters and is shallow in resource consumption—requiring minimal size, weight and power. Additionally, it can scale up as a constellation of receivers for faster coverage, making this innovative remote-sensing mode highly useful.
Image Credit: ISRO