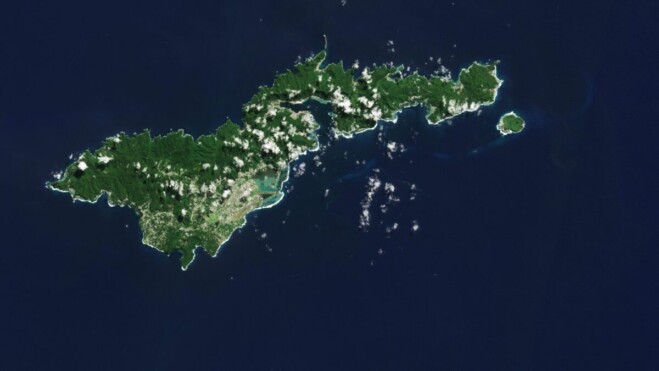
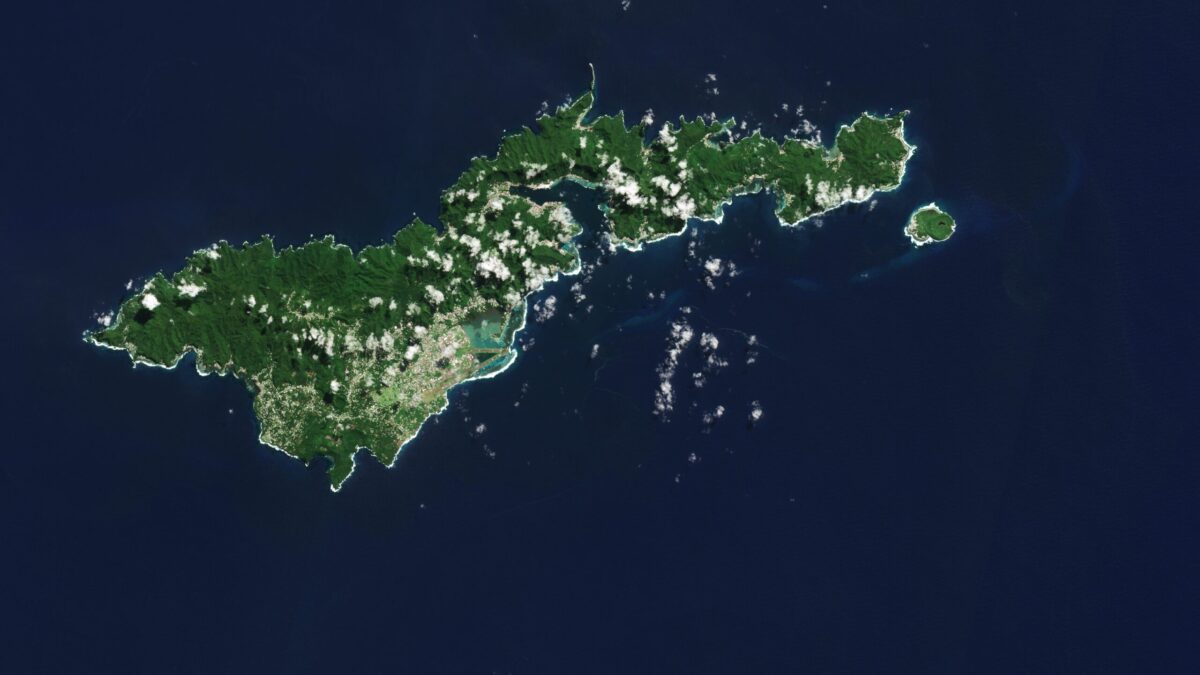
The Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission captured an amazing view of the tropical island of Tutuila, the largest in the American Samoa archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean.
American Samoa is an unincorporated territory of the United States and is part of the Samoan Islands chain, situated some 4,000 kilometers southwest of Hawaii and about 3,000 kilometers northeast of New Zealand. The eastern part of the chain of islands forms the American Samoa, while the western part forms the independent state of Samoa.
American Samoa comprises five volcanic islands: Tutuila, Aunu’u, Tau, Ofu and Olosega; and two coral atolls, Rose and Swains.
Tutuila is a small, narrow island and home to many volcanic mountains. At 653 meters, Mount Matafao, which lies in the centre of the island, is the highest. The mountain range, which cuts across the island, is rugged with steep cliffs dominating the northern part of the island. The south is flatter. Coral reefs create barriers to the open sea, resulting in lagoons, visible in turquoise, prominent off the southern coast.
Image Credit: Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2023), processed by ESA