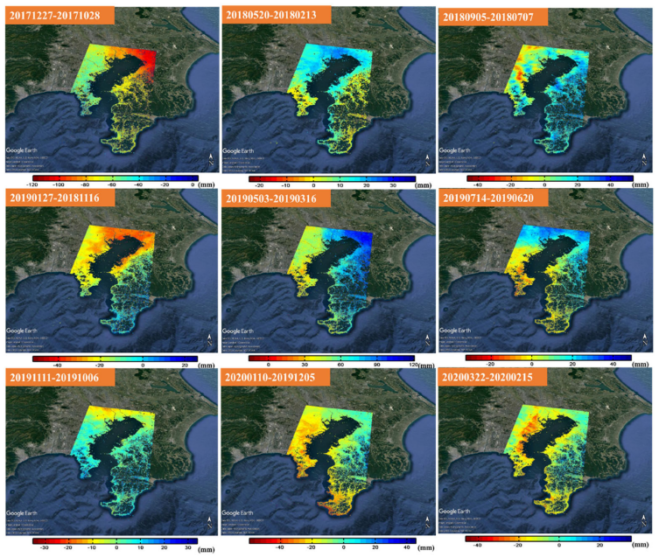
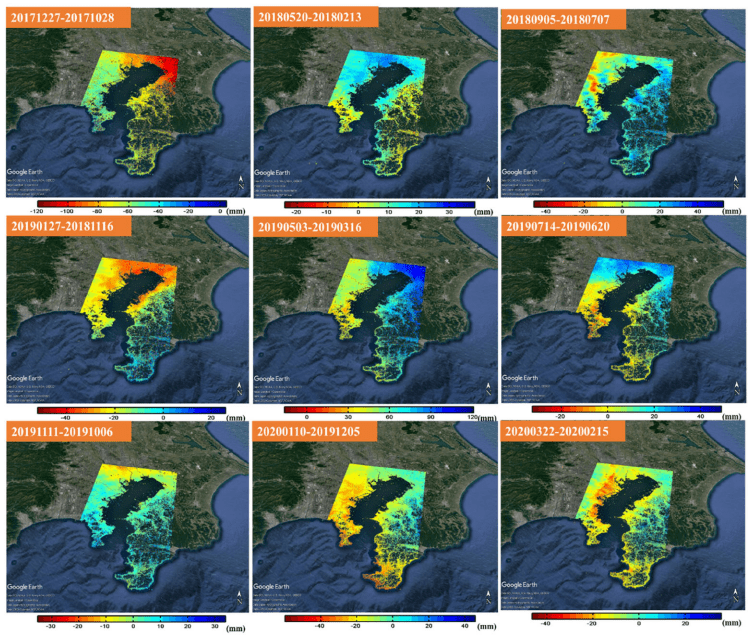
Land subsidence causes Earth’s surface to sink, flooding coastal areas and damaging infrastructure. It can be monitored using observation wells, global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), and interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR). Given its accuracy and applicability, researchers have recently utilized consecutive differential InSAR to investigate subsidence in the Kanagawa prefecture in Japan. The results were consistent with observation well and GNSS data, indicating its potential for substituting other monitoring techniques.
Land subsidence is a phenomenon wherein the Earth’s surface sinks downwards. It occurs mainly due to human activities, such as excessive groundwater extraction. It is a major global concern, affecting 19% of the world’s population. In Japan, some parts of the Tokyo metropolitan region are already sinking. This process can accelerate the flooding of coastal areas and cause damage to buildings and infrastructure. Therefore, monitoring land subsidence is crucial.
In Japan, observation wells are utilized to measure changes in the land surface and groundwater levels every few months. Additionally, the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is also popular. However, observation wells are more reliable because atmospheric effects can modify GNSS observations. Observation wells require regular maintenance of their machines, which is expensive. Further, there is an anticipated shortage of engineers qualified to undertake the job as the Japanese population gets older with a declining birth rate. In this light, a new land subsidence monitoring technique—interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR)—is gaining attention.
Click here for more information.