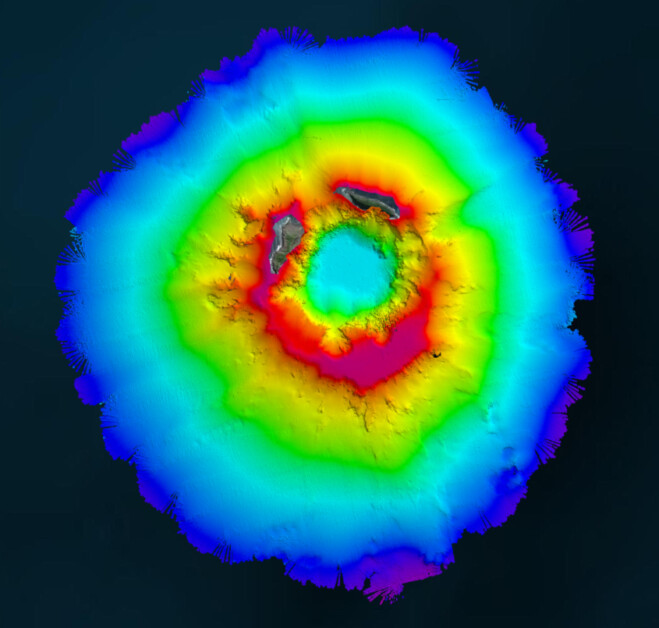
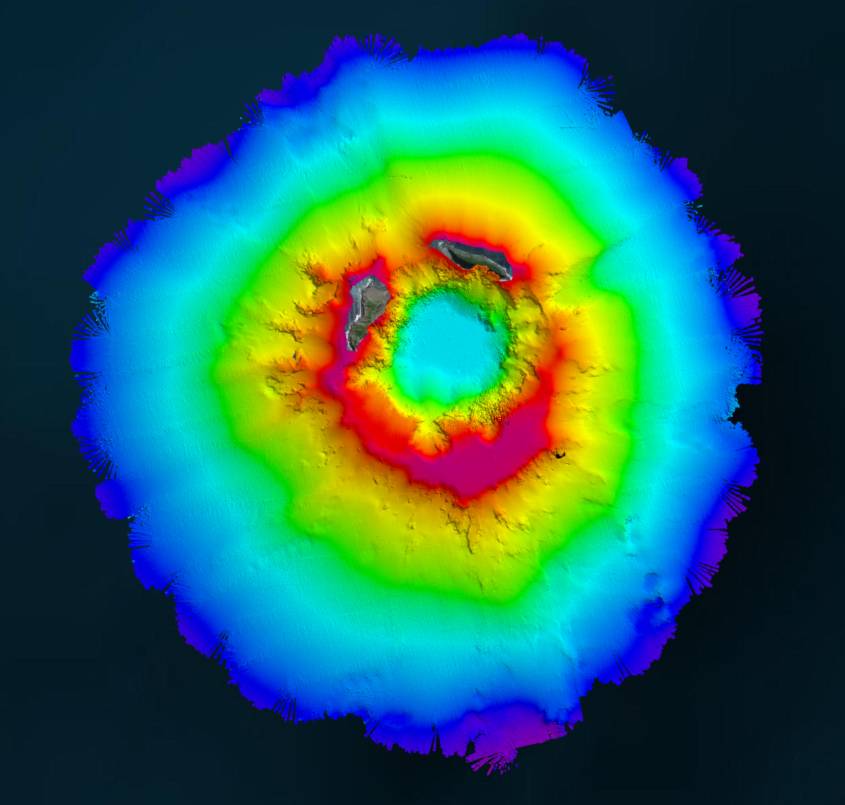
In April 2022, New Zealand’s National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA) and The Nippon Foundation announced a mission to discover the undersea impacts of the Hunga-Tonga Hunga-Ha’apai (HT–HH) volcanic eruption, which produced the biggest atmospheric explosion recorded on Earth in over a century. Supported by The Nippon Foundation-GEBCO Seabed 2030 Project, TESMaP had two phases, led by NIWA: phase one saw scientists survey the area around the volcano with RV Tangaroa. As part of phase two, SEA-KIT International’s Uncrewed Surface Vessel (USV) Maxlimer was used to conduct further mapping inside the caldera.
For the duration of TESMaP, Seabed 2030 and Nippon Foundation-GEBCO Ocean Mapping Fellows utilized software provided by Teledyne CARIS (based in Fredericton, New Brunswick)—a Seabed 2030 partner with over 40 years of experience in developing hydrographic and marine geospatial software. The software was integral to the project as they facilitated the monitoring of data quality and coverage, with new data being used for comparative studies against previous maps to assess the effects of the eruption on marine life and seafloor composition. Software provided by Teledyne CARIS will also be used to process the data to generate the final products.