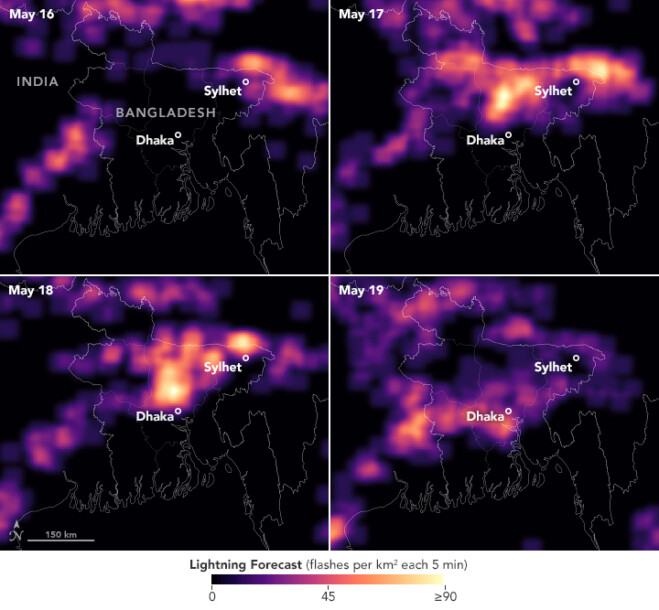
Bangladesh has a long history of deadly and costly storms. Among the most worrisome are kalbaishakhi, small but powerful storm cells that tend to affect the country in the spring. Kalbaishakhi were responsible for a 1989 tornado that is believed to be the deadliest in world history, as well as a lightning strike at a wedding party in 2021 that caused 17 deaths. Because these storms are so localized, they can be notoriously difficult to forecast, especially without access to the most advanced weather prediction technology.
“Bangladesh is a hotspot for high-impact weather events—intense rainfall, damaging wind and hail, frequent lightning strikes, and cyclones,” said Azizur Rahman, director of the Bangladesh Meteorological Department (BMD). “And the science is clear: Because of climate change, these high-impact weather events will be more frequent and more intense in the future.”
Researchers have created a new tool to boost the country’s ability to forecast kalbaishakhiand other severe weather. The U.S.-based SERVIR program and the BMD recently launched the High-Impact Weather Assessment Toolkit (HIWAT), a web-based tool that integrates data from NASA’s Earth-observing satellites with BMD’s local observations in order to improve weather forecasts. The project was led by Patrick Gatlin, a research meteorologist at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, with SERVIR’s Hindu-Kush Himalaya team at the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD).
Image Credit: NASA Earth Observatory image by Lauren Dauphin, using data from the High Impact Weather Assessment Toolkit (HIWAT) team at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and the NASA SERVIR Applied Sciences Team