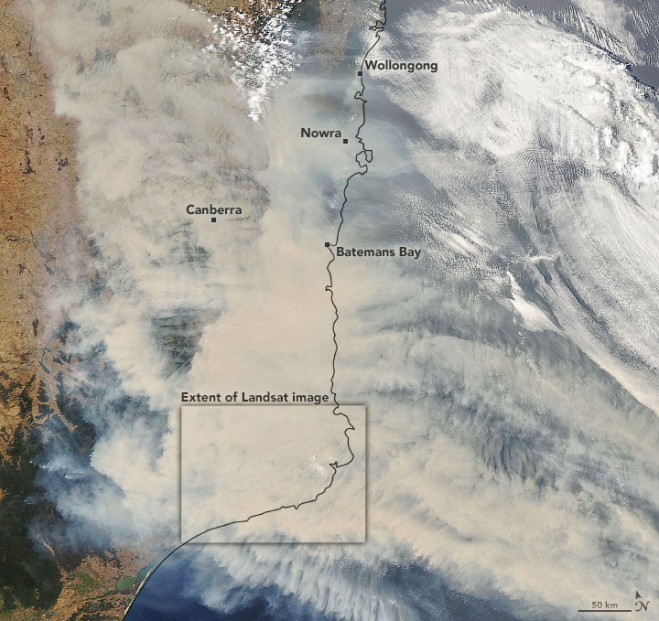
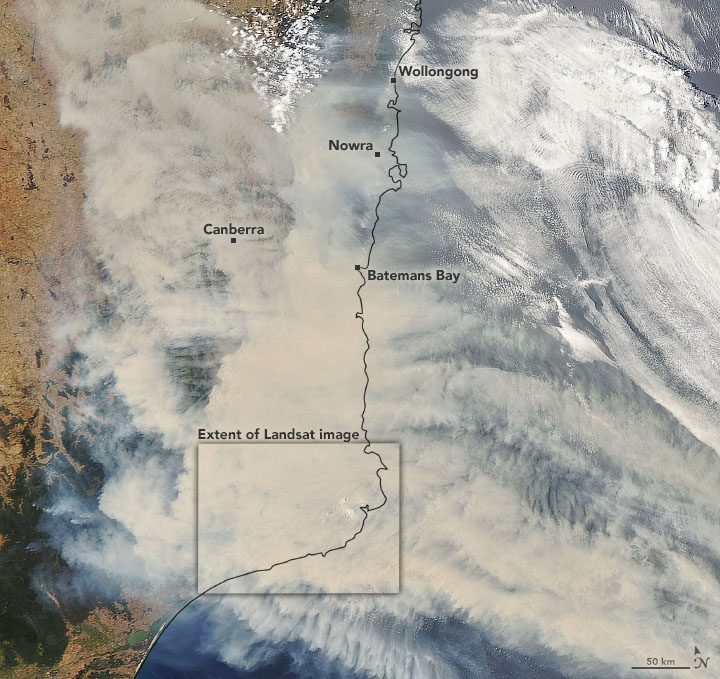
The record-setting and deadly fire season in Australia took a dramatic turn in the last week of December and first week of January. Residents of southeastern Australia told news media about the daytime seeming to turn to night, as thick smoke filled the skies and intense fires drove people from their homes.
On Jan. 1, 2020, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 acquired a natural-color image of thick smoke blanketing southeastern Australia along the border of Victoria and New South Wales.
According to international and Australian media sources, at least 1,200 homes in Victoria and New South Wales have been destroyed by fires this season, which began early in the spring and has not subsided. Media have reported that at least 18 people have died and more than 5.9 million hectares (14.6 million acres) have burned. Air quality indices in southeastern Australia and as far east as New Zealand have been near or above the highest reportable levels.
In a late December 2019 report, the Australian Bureau of Meteorology reported that its Forest Fire Danger Index (FFDI)—which blends data on air temperatures, humidity, precipitation, winds and other factors—has been well above average for 95 percent of the nation. More than 60 percent of Australia set record highs for fire danger this season, and the summer is only just underway.
Image Credit: NASA Earth Observatory images by Joshua Stevens, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey and MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS/LANCE and GIBS/Worldview.