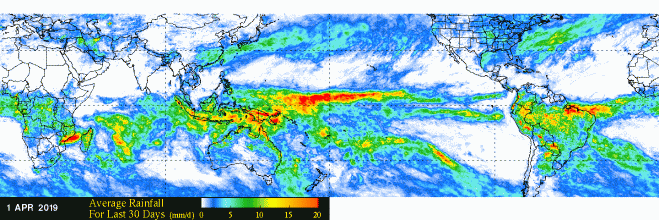
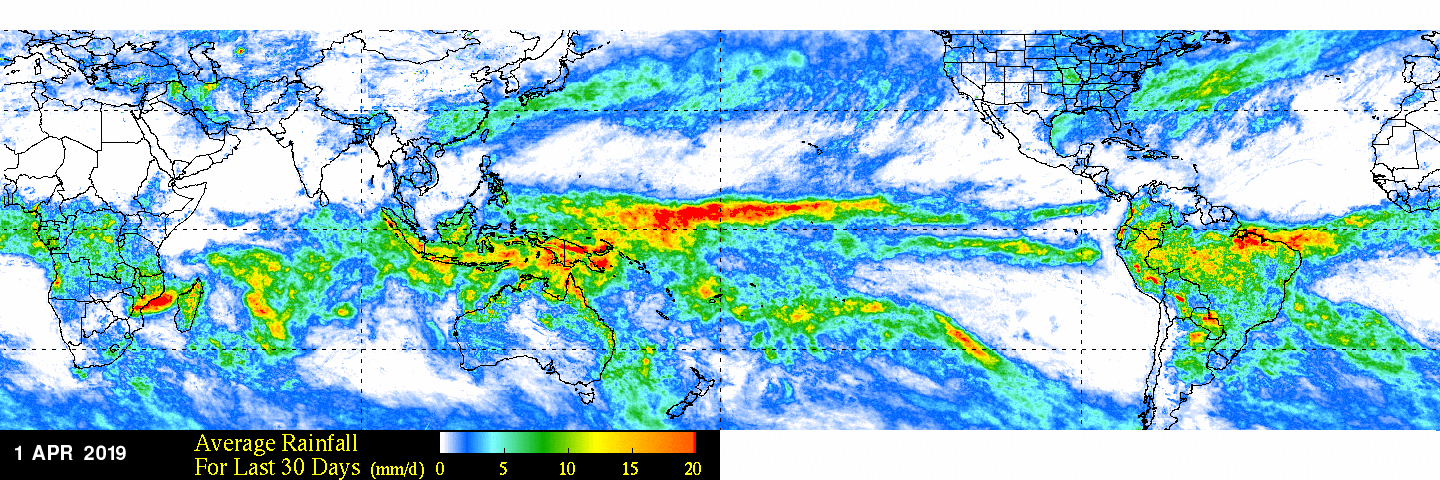
An El Niño that began to form last fall has matured and is now fully entrenched across the Pacific Ocean. Changes in sea surface temperatures (SSTs) brought about by an El Niño affect the atmosphere, resulting in distinctive changes in the rainfall pattern across the Pacific Basin. These changes show up as anomalies or deviations in NASA’s analysis of climatological rainfall.
In a typical El Niño, warmer than average SSTs off the coast of Peru lead to enhanced convection (rising air that condenses and forms clouds and storms) and above-average rainfall in the eastern Pacific near to the Equator, and lower-than-average rainfall over the western Pacific.
However, recent estimates of monthly average rainfall and corresponding rainfall anomalies show heavy rain and above-average rainfall located across the Equatorial Central Pacific, not the eastern Pacific. This is known as El Niño “Modoki” (Japanese for “a similar but different thing”) or a Central Pacific El Niño, wherein enhanced SSTs and rainfall occur near the dateline and not near the coast of Peru.