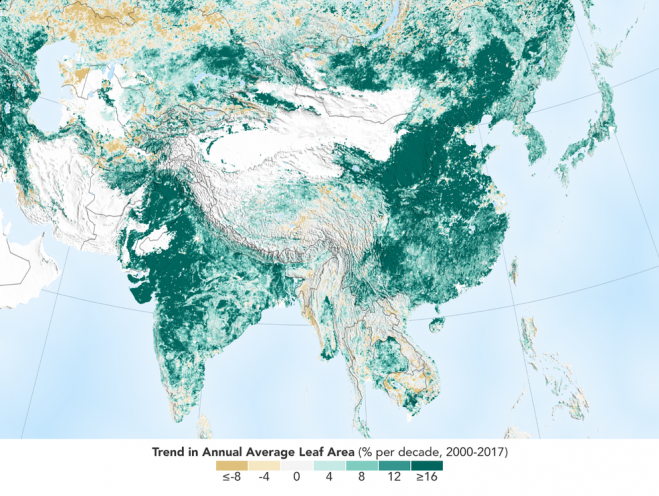
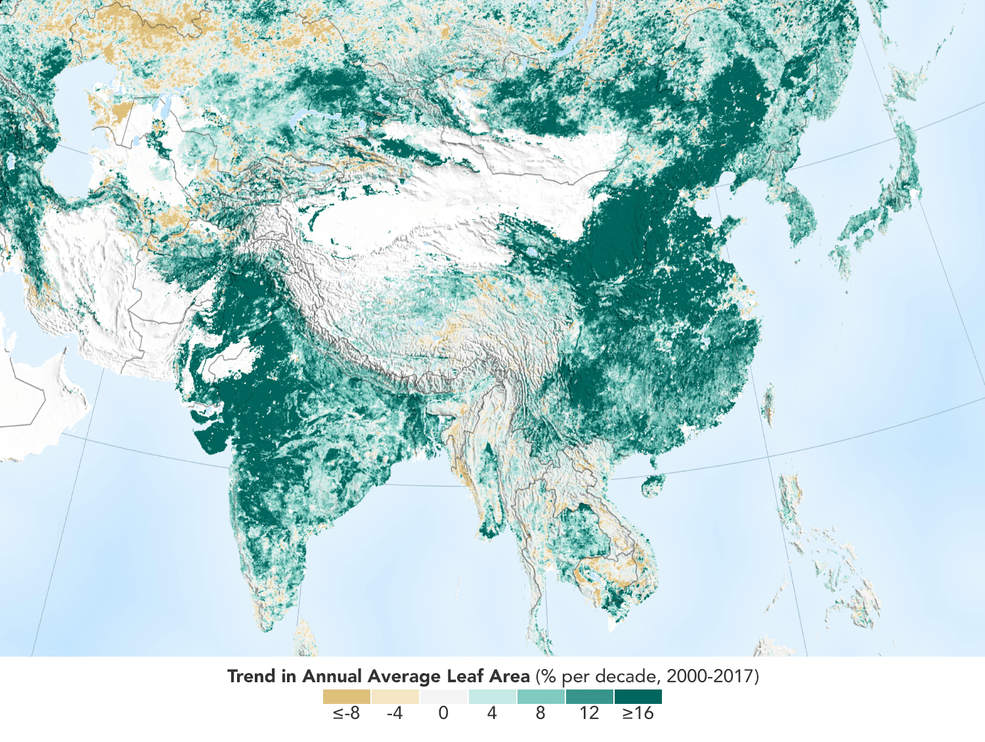
The world is literally a greener place than it was 20 years ago, and data from NASA satellites revealed a counterintuitive source for much of this new foliage: China and India. A new study shows that the two emerging countries with the world’s biggest populations are leading the increase in greening on land. The effect stems mainly from ambitious tree-planting programs in China and intensive agriculture in both countries.
The greening phenomenon was first detected using satellite data in the mid-1990s by Ranga Myneni of Boston University and colleagues, but they did not know whether human activity was one of its chief, direct causes. This new insight was made possible by a nearly 20-year-long data record from a NASA instrument orbiting the Earth on two satellites. It’s called the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, and its high-resolution data provides very accurate information, helping researchers work out details of what’s happening with Earth’s vegetation, down to the level of 500 meters, or about 1,600 feet, on the ground.
Image Credit: NASA Earth Observatory