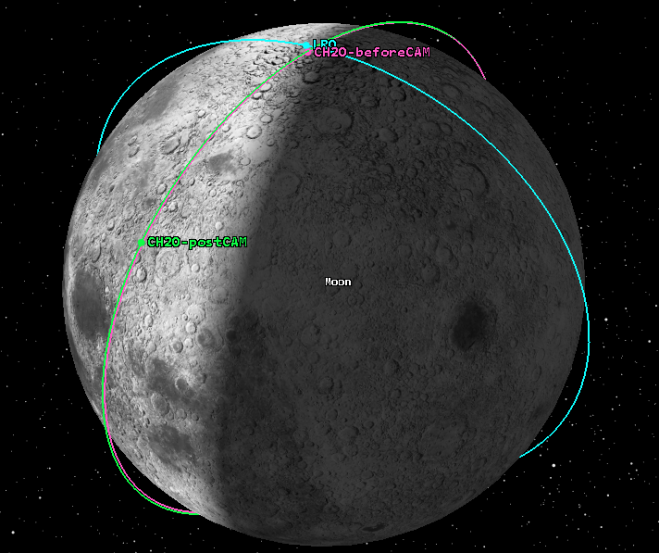
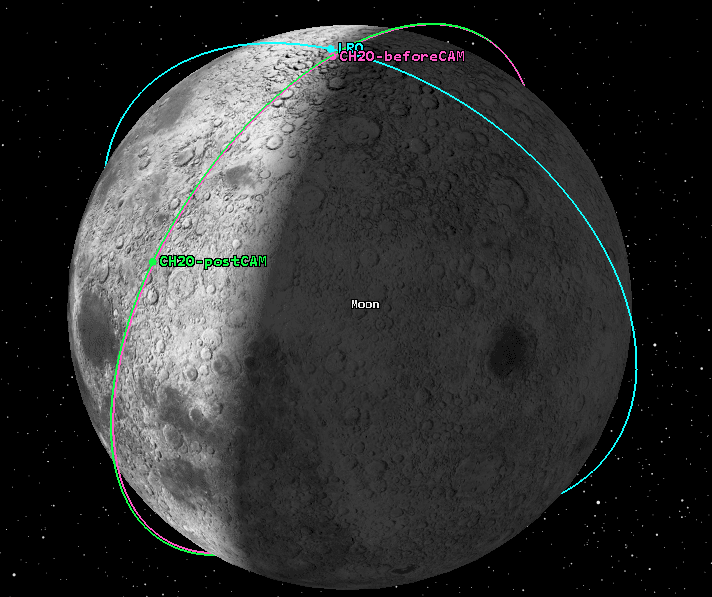
A very close conjunction between Chandrayaan-2 Orbiter (CH2O) and Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) of NASA was expected to occur on Oct. 20, 2021, near the Lunar North pole. During a span of one week prior, analyses by ISRO and JPL/NASA consistently showed that the radial separation between the two spacecraft would be less than 100 meters, and the closest approach distance would be only about 3 kilometers at the aforementioned time of closest approach.
Both agencies deemed the situation warranted a collision avoidance maneuver (CAM) to mitigate the close approach risk, and it was mutually agreed that CH2O would undergo the CAM. The maneuver was executed on Oct. 18, 2021, and was designed to ensure a sufficiently large radial separation at the next-closest conjunction between the two spacecraft. After orbit determination of CH2O with post-maneuver tracking data, it was reconfirmed that there would be no further close conjunctions with LRO in the near future with the achieved orbit.
Image Credit: ISRO