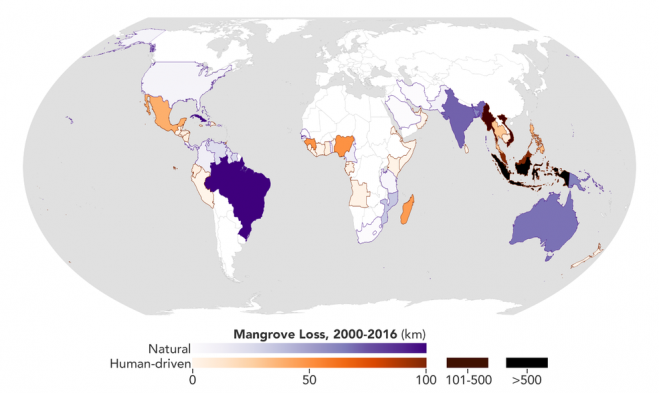
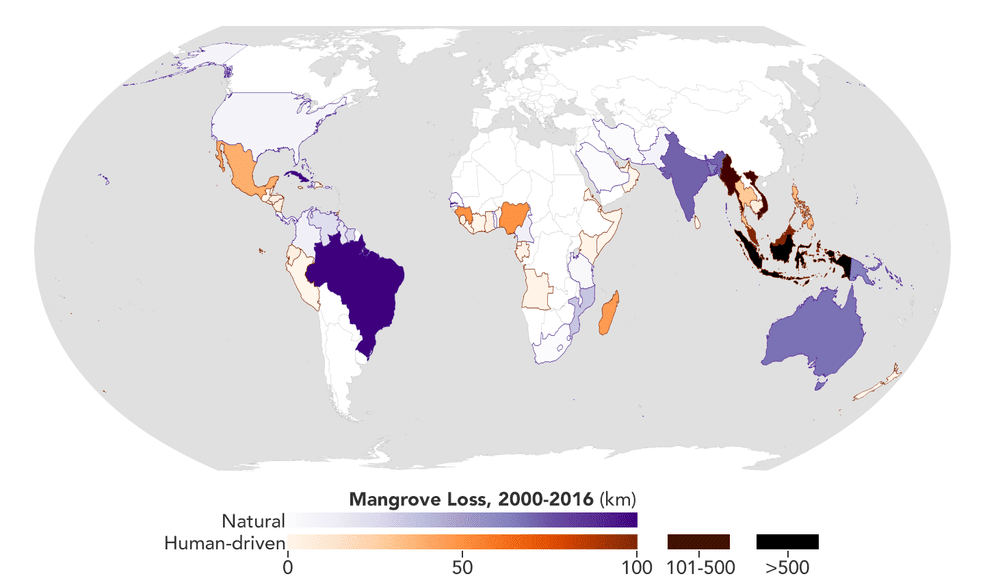
Using high-resolution data from the joint NASA-U.S. Geological Survey Landsat program, researchers have created the first map of the causes of change in global mangrove habitats between 2000 and 2016—a valuable tool to aid conservation efforts for these vital coastline defenders.
Mangroves are hardy trees and shrubs that grow in the salty, wet, muddy soils of Earth’s tropical and subtropical coastlines. They protect the coastlines from erosion and storm damage; store carbon within their roots, trunks, and in the soil; and provide habitats for commercially important marine species. The study showed that overall, mangrove habitat loss declined during the period. However, losses from natural causes like erosion and extreme weather declined more slowly than human causes such as farming and aquaculture. For conservation and resource managers trying to prevent loss or re-establish new habitats, this finding highlights the need for strategies that account for natural causes of loss.
The global map will benefit researchers investigating the carbon cycle impacts of mangrove gain and loss, as well as help conservation organizations identify where to protect or restore these vital coastal habitats.
Image Credit: NASA Earth Observatory/Joshua Stevens