Bushfires have raged in Victoria and New South Wales since November 2019, yielding startling satellite images of smoke plumes streaming from southeastern Australia on a near daily basis. The images got even more eye-popping in January 2020 when unusually hot weather and strong winds supercharged the fires.
Narrow streams of smoke widened into a thick gray and tan pall that filled the skies on January 4, 2020. Several pyrocumulus clouds rose from the smoke, and the towering clouds functioned like elevators, lifting huge quantities of gas and particles well over 10 kilometers (6 miles) above the surface—high enough to put smoke into the stratosphere.
During the past few weeks, satellite sensors have collected data that is even more stunning than the images. The Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) on NASA’s Aura satellite has collected preliminary data that suggests the Australian fires injected more carbon monoxide into the stratosphere in the month of January than any other event the sensor has observed outside of the tropics during its 15-year mission. The fires appear to have produced about three times as much of the poisonous, colorless gas as major fires in British Columbia in 2017 and Australia in 2009. (Fires in Indonesia in 2015-16 may have delivered as much or more, but those fires happened over a longer period.)
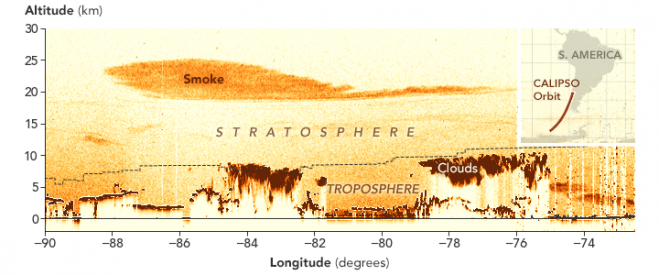
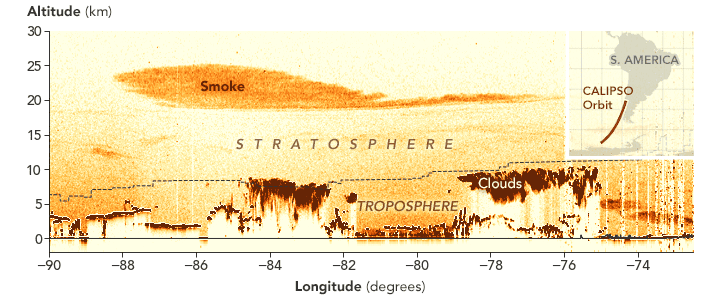
The Australian smoke is also proving to be an outlier in measurements made by the NASA/CNES CALIPSO satellite, which carries a sensor that scientists use to track the height of the smoke plume. On Jan. 6, 2020, a few days after the most explosive fire activity, CALIPSO measured smoke between 15 and 19 kilometers (9 and 12 miles) above the surface.
Within two weeks, the top of the plume had risen as high as 25 kilometers, making this the highest wildfire-caused plume ever tracked by CALIPSO. “The plume is rising because of the radiative heating of soot particles within the smoke by the Sun,” explained Jean-Paul Vernier, a scientist from the National Institute of Aerospace at NASA Langley Research Center and the lead of a NASA disasters team responding to the fires.