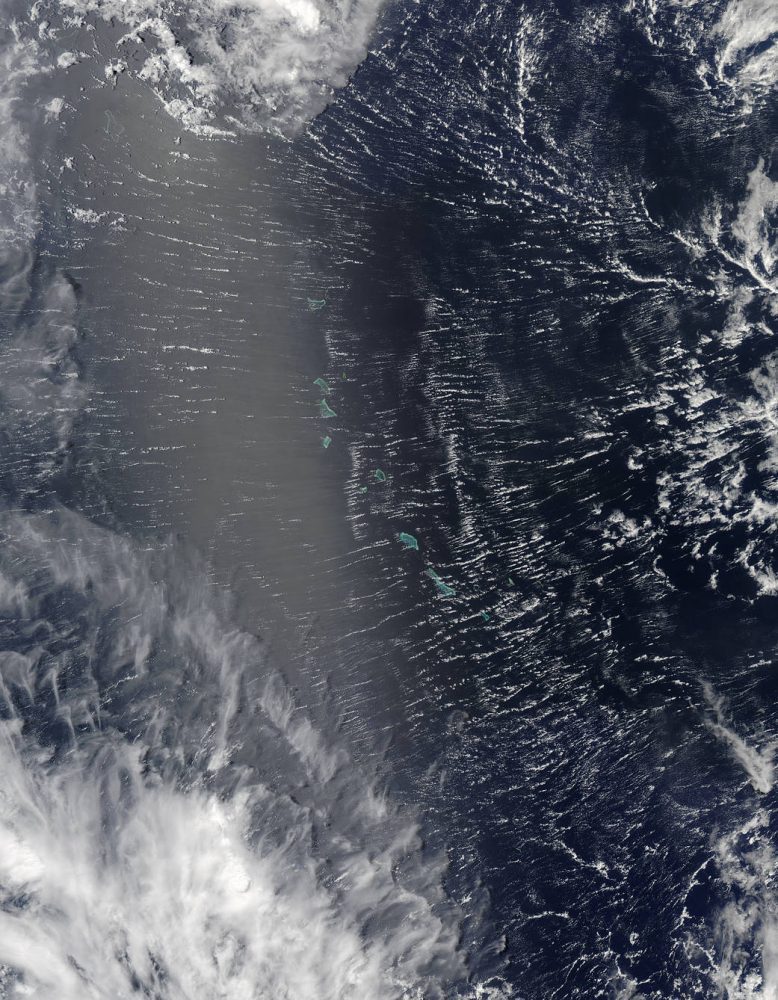
Areas near the equator are frequently cloudy, obscuring the view of Earth’s surface from space. April 7, 2017, was no different. On that day, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this natural-color image of clouds over the Gilbert Islands. The remote island chain is part of the Republic of Kiribati, and straddles the equator in the central Pacific Ocean.
These clouds, however, were not a typical tropical rainstorm. Instead, the parallel “roll clouds” were likely influenced by the development of Tropical Cyclone Cook to the south. At the time, Cook was strengthening near Vanuatu and heading toward New Caledonia.
“As far as tropical cyclones go, we believe that they are a nearly ideal environment for roll formation,” said Ralph Foster, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Washington. The extreme wind shear associated with cyclones generates additional turbulence in the already turbulent layer of air near Earth’s surface. According to Foster, the turbulent flow in this layer “self-organizes,” forming long rolls of counter-rotating air.
More precisely, the atmosphere has alternating clockwise and counterclockwise circulation. In between the overturning circulations are updrafts and downdrafts. If conditions are right for clouds to form, clouds will grow in the updraft zone and be suppressed in the downdraft. The resulting linear cloud features can persist for hours.